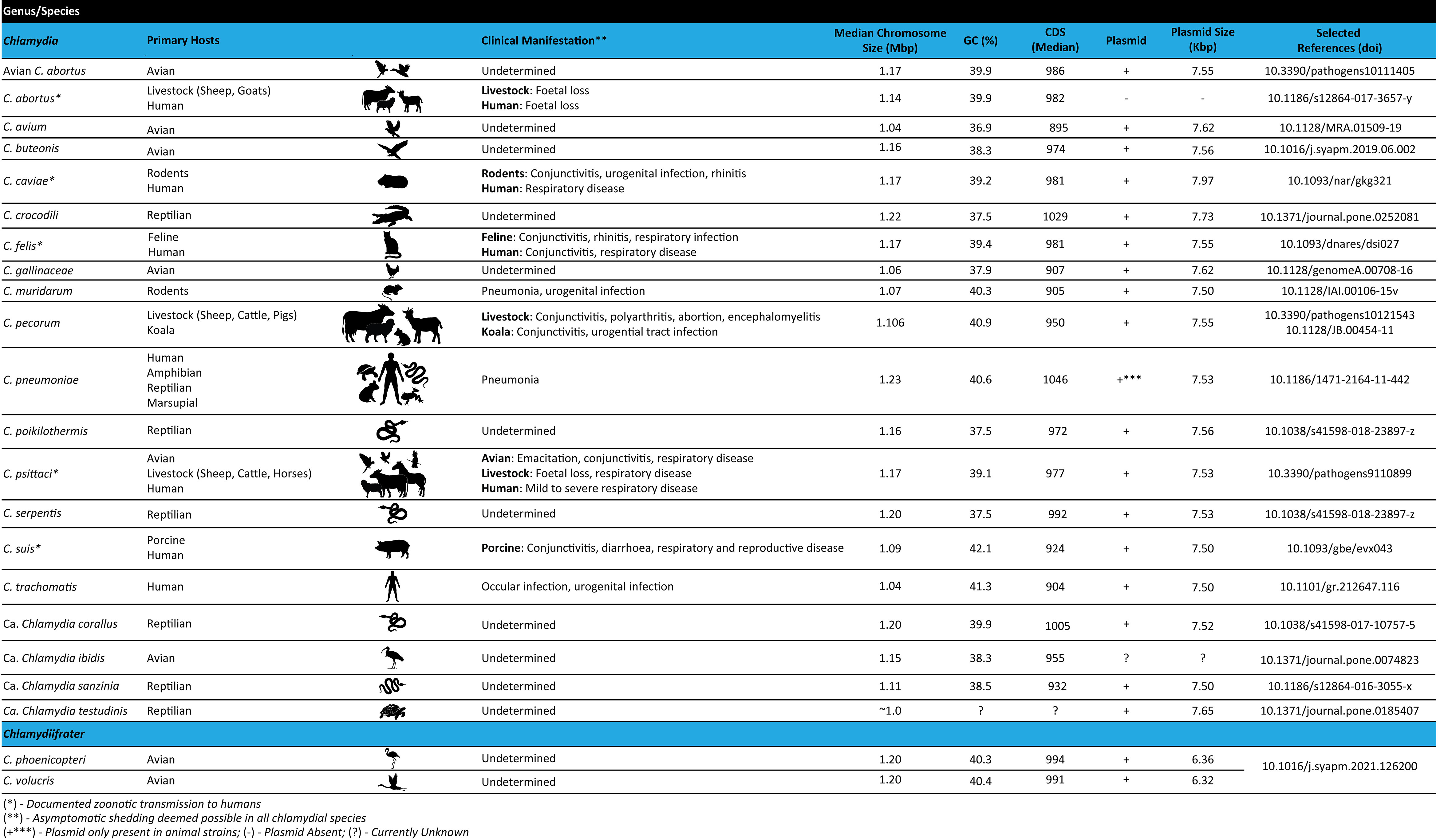
Frontiers Genome organization and genomics in Chlamydia: whole genome sequencing increases understanding of chlamydial virulence, evolution, and phylogeny
4.5
$ 11.50
In stock
(310)
Product Description

Comparative genomic analysis of human Chlamydia pneumoniae isolates from respiratory, brain and cardiac tissues - ScienceDirect
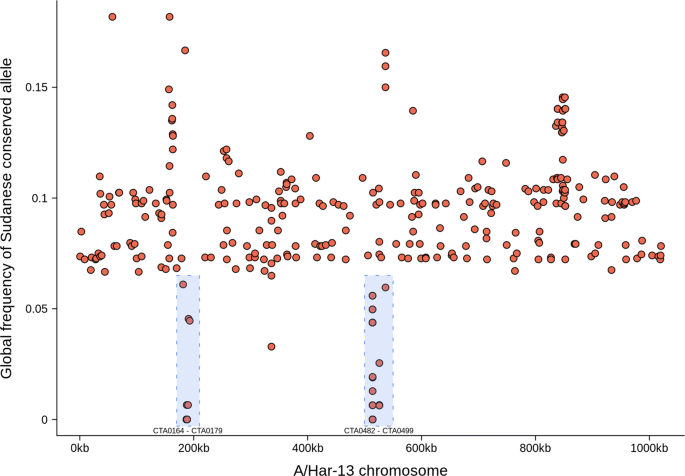
Whole-genome sequencing of ocular Chlamydia trachomatis isolates from Gadarif State, Sudan, Parasites & Vectors

Integrating metagenomic and amplicon databases to resolve the phylogenetic and ecological diversity of the Chlamydiae
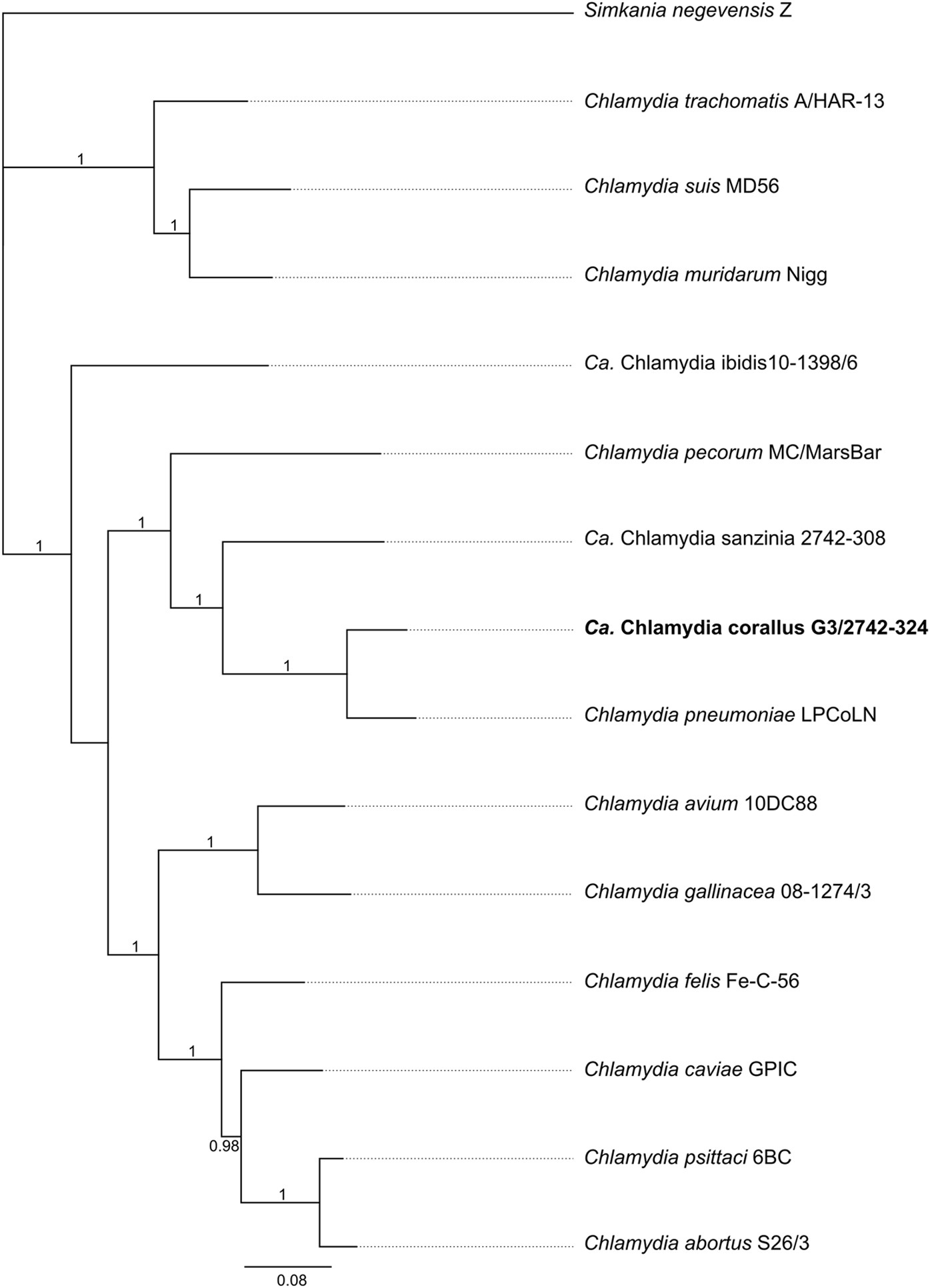
Culture-independent metagenomics supports discovery of uncultivable bacteria within the genus Chlamydia
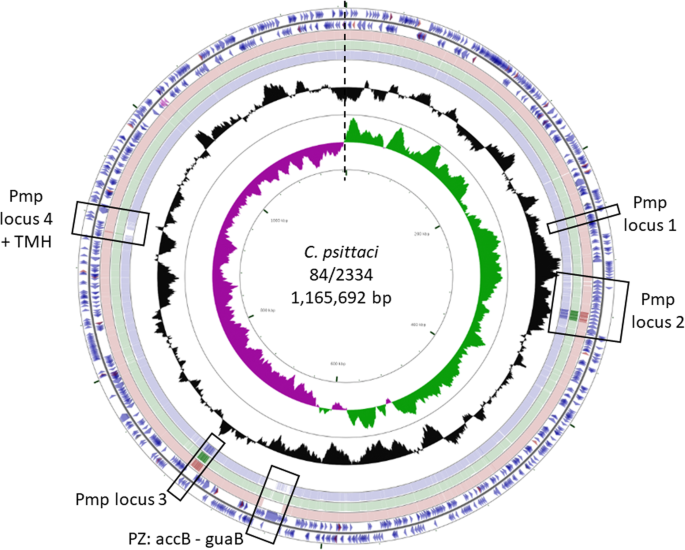
Whole genome de novo sequencing and comparative genomic analyses suggests that Chlamydia psittaci strain 84/2334 should be reclassified as Chlamydia abortus species, BMC Genomics

Timeline for Chlamydia spp., Brucella spp. and Legionella spp. during

The chlamydial developmental cycle. (1) Adhesion to host cells by C.
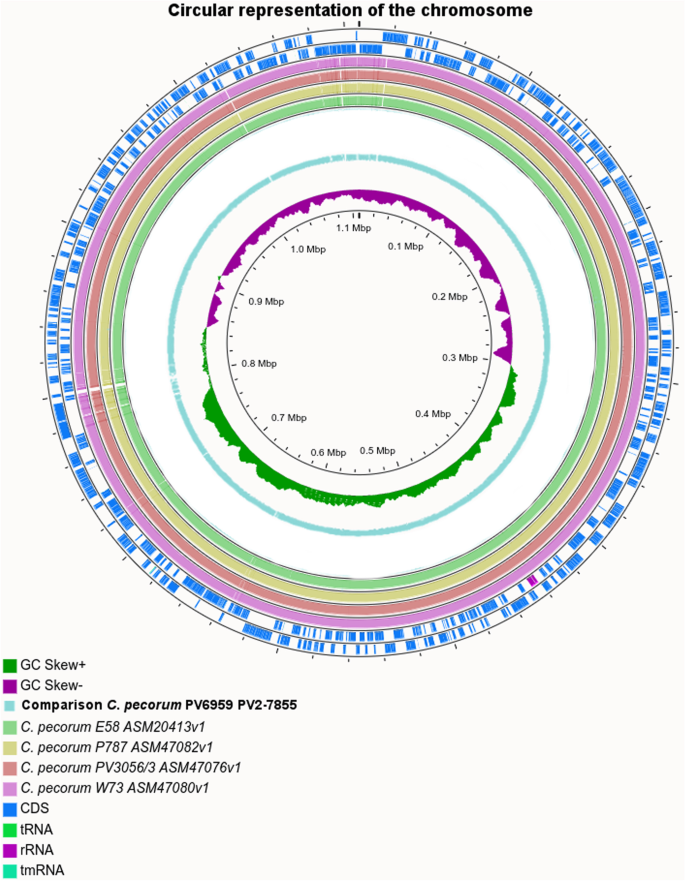
Comparative analysis of two genomes of Chlamydia pecorum isolates from an Alpine chamois and a water buffalo, BMC Genomics
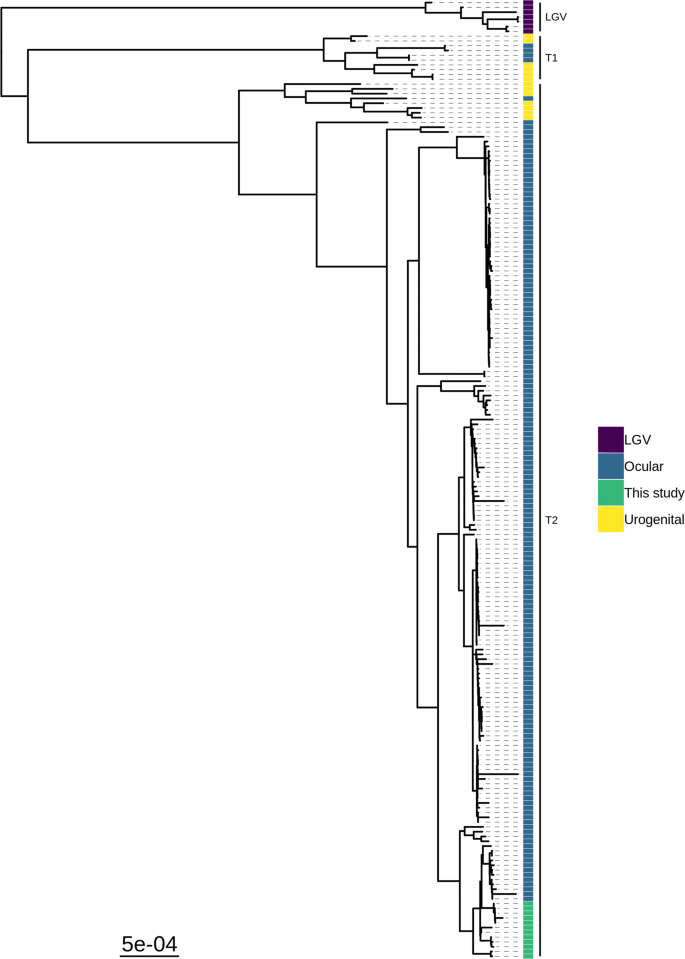
Whole-genome sequencing of ocular Chlamydia trachomatis isolates from Gadarif State, Sudan, Parasites & Vectors
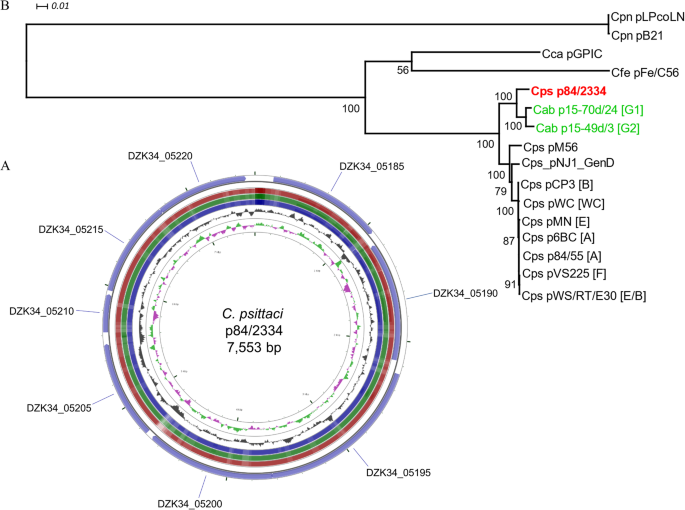
Whole genome de novo sequencing and comparative genomic analyses suggests that Chlamydia psittaci strain 84/2334 should be reclassified as Chlamydia abortus species, BMC Genomics

Evolution, phylogeny, and molecular epidemiology of Chlamydia - ScienceDirect









